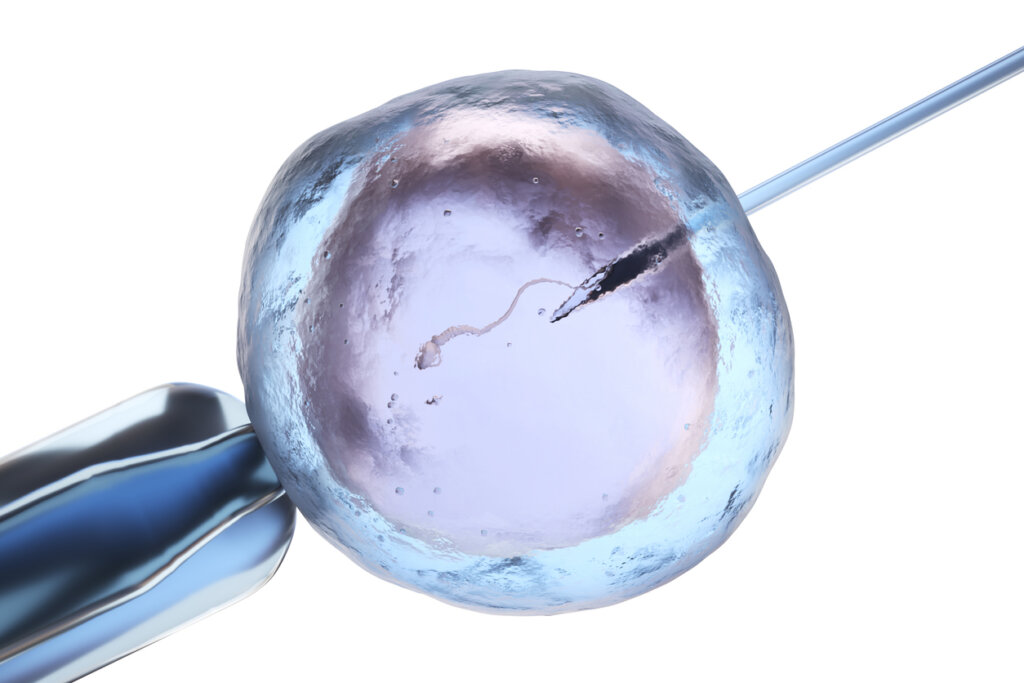
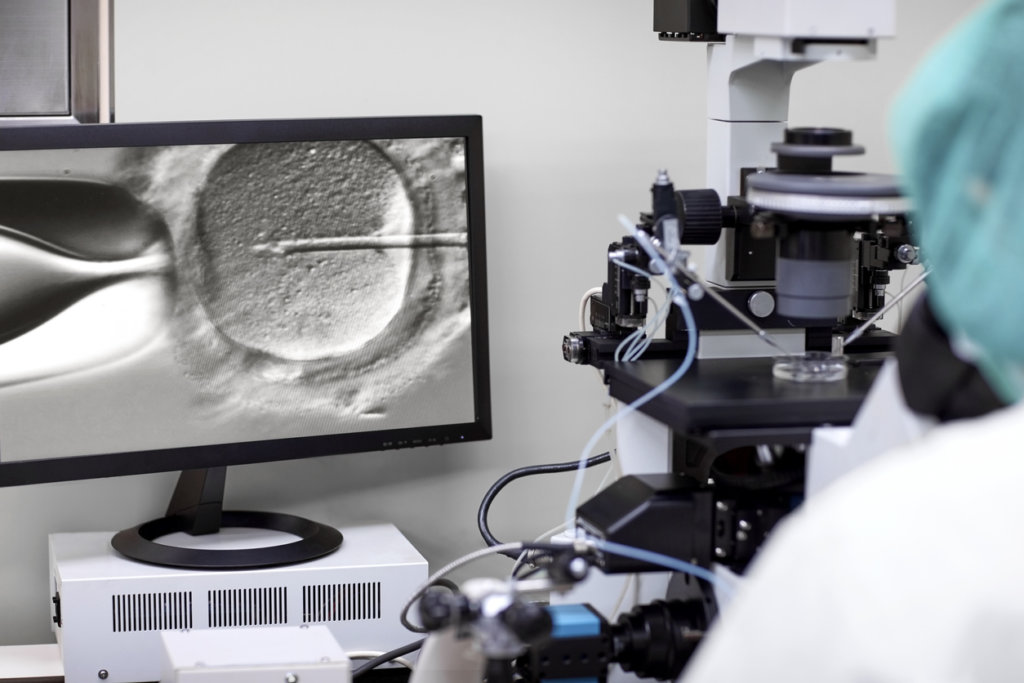
In the ICSI process, a tiny needle, called a micropipette, is used to inject a single sperm into the center of the egg.
Category Archives: Medical
One of the essential parts of the in vitro fertilization process is transferring the fertilized embryo. It helps to know what to expect, along with some of the risks and precautions to keep in mind. Here is some information on how the embryo transfers process works and for whom embryo transfers are an option.
Fresh and Frozen Embryo Transfers: An embryo transfer is the final step of the In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) process. During a fresh transfer, the embryo is transferred back into the uterus without ever being frozen. A frozen embryo transfer (FET) is a cycle in which frozen embryos from a previous IVF or donor egg cycle are thawed and then transferred.
Follicle-stimulating hormone, also known as FSH, is a hormone checked routinely between days 2-4 of the menstrual cycle. It is produced by the pituitary gland to stimulate the ovaries to develop follicles. As a dominant follicle develops, it in turn sends certain signals (inhibin-B) that will suppress FSH release (negative feedback).
By collecting family health history and having this information early, people are able to access the growing number of genetic tests available, expand their options for family planning, improve the management of pregnancy or neonatal care, and take advantage of treatments for inherited disease
Carrier screening is a type of genetic test that can tell you whether you carry a gene for certain genetic disorders. When it is done before or during pregnancy, it allows you to find out your chances of having a child with a genetic disorder
Everyone’s fertility experience is different, and having a financial plan personalized to fit your needs, should be flexible and built just for you.
Anti-Müllerian Hormone (AMH)
A hormone secreted by the cells of the developing antral and pre-antral follicles (or egg sacks) in the ovaries. Once secreted from these growing follicles, AMH stops more immature ones from getting recruited into the maturation process, so that not all the eggs mature all at the same time. Because AMH reflects the number of eggs maturing in the ovaries on their way to ovulation, AMH is a strong indicator of a woman’s ovarian reserve (OR) – the ovaries’ ability to produce good-quality eggs. Using the Roche Elecsys AMH Assay, the median AMH level (pmol/l) for a donor between 20–29 years of age is 13.1 – 53.8.
During IVF it is normal to see a continual drop in numbers in embryo development, which, can lead to the best embryos that will give you your baby.
The appearance or grade of the blastocyst can be used to predict the chance of pregnancy. A blastocyst with a higher grade has a better chance of implanting than one with a lower grade.